中国组织工程研究 ›› 2018, Vol. 22 ›› Issue (26): 4179-4183.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.0889
• 材料生物相容性 material biocompatibility • 上一篇 下一篇
人脱细胞真皮复合骨髓间充质干细胞构建组织工程皮肤修复皮肤创面缺损
池 凯,毋 磊,陈龙金,李永林
- 郑州市第一人民医院整形外科,河南省郑州市 450000
Tissue-engineered skin for skin wound repair: construction by human acellular dermal matrix combined with bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells
Chi Kai, Wu Lei, Chen Long-jin, Li Yong-lin
- Department of Plastic Surgery, the First People’s Hospital of Zhengzhou, Zhengzhou 450000, Henan Province, China
摘要:
文章快速阅读:
.jpg)
文题释义:
脱细胞真皮基质:是由动物或人类皮肤制成的无细胞组织薄片。它去除了皮肤的全层表皮及真皮层中的全部细胞成分,而保留了真皮的胶原成分和组织基本结构,同时也保留了基底膜成分。由于皮肤移植中的排斥反应主要是由细胞免疫引起,在去除了具有较强原性的细胞成分后,以胶原蛋白为主要成分的脱细胞真皮基质本身抗原性很低,几乎不引起宿主的排斥反应,可以在宿主体内长期存留并最终被降解和引导正常组织重建。
角蛋白:属于细胞支架蛋白质类,它通过形成中间纤维网络维持上皮细胞和组织的完整性。角蛋白19作为细胞中间丝的重要组成能起到维持细胞形态的作用。细胞角蛋白19是检测表皮干细胞的重要指标,在正常皮肤的基底层细胞呈阳性表达,在皮肤鳞状细胞癌中的表达与细胞的分化程度有关,分化越低表达越强,分化越高表达越弱,甚至不表达。
背景:构建组织工程皮肤的种子细胞和支架材料多种多样,探索更为合适的构建方法亦是国内外专家学者争相研究的热点。
目的:探讨组织工程皮肤促进大鼠皮肤缺损创面愈合的可行性。
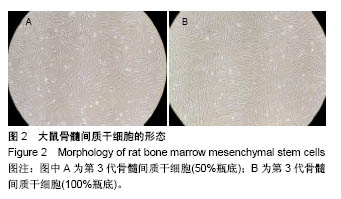
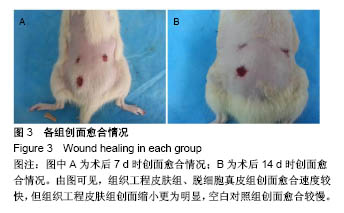
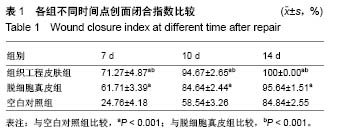
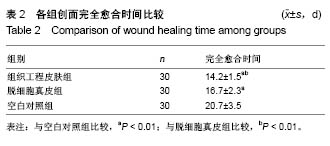
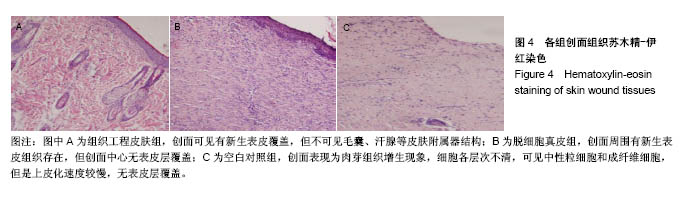
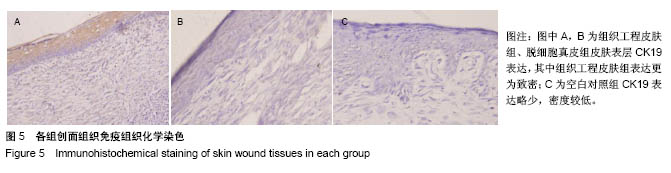
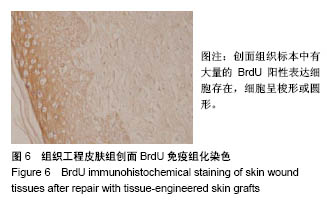
方法:选用6-8周龄SD大鼠,采用全骨髓贴壁培养法分离、培养、纯化骨髓间充质干细胞。利用人包皮为材料,采用酶消化法制作脱细胞真皮。以骨髓间充质干细胞为种子细胞,脱细胞真皮为支架材料,构建组织工程皮肤,将其覆盖于SD大鼠皮肤缺损创面,另设置单纯移植脱细胞真皮组和空白对照组。记录创面愈合时间并计算创面闭合指数。移植2周后创面取材行苏木精-伊红染色,CK19及BrdU免疫组织化学染色,以评价创面的愈合情况。
结果与结论:①3组创面闭合指数:组织工程皮肤组>脱细胞真皮组>空白对照组,组间两两比较差异均有显著性意义(P < 0.05);②3组创面愈合时间:组织工程皮肤组<脱细胞真皮组<空白对照组,组间两两比较差异均有显著性意义(P < 0.05);③组织工程皮肤组有BrdU阳性细胞表达,组织工程皮肤组CK19表达显著高于脱细胞真皮组、空白对照组;④结果表明,应用骨髓间充质干细胞与脱细胞真皮构建的组织工程皮肤对全层皮肤缺损创面具有很好的促进愈合作用。
ORCID: 0000-0002-1011-7187(池凯)
中图分类号:
.jpg)
.jpg)